erp sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The concept of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is pivotal in today’s business landscape, serving as an integrated management system that streamlines processes and information across various departments. Understanding the core functions and the types of ERP systems available can significantly impact organizational efficiency and decision-making.
As businesses continue to evolve, the significance of ERP becomes increasingly evident, enabling organizations to adapt and thrive in a competitive market. This comprehensive overview will explore the fundamentals of ERP, effective implementation strategies, diverse modules and features, and the promising future trends that are set to redefine the ERP landscape.
ERP Fundamentals
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are integrated software platforms that manage and streamline a company’s core business processes across various departments. By consolidating data and workflows into a single system, ERP enables organizations to operate more efficiently, make informed decisions, and improve overall productivity.The core functions of ERP include managing finance, human resources, supply chain, customer relationship management, and manufacturing processes.
These systems provide real-time data and analytics, which help businesses to optimize their operations and respond swiftly to market changes. By integrating different business functions, ERP systems facilitate a seamless flow of information throughout the organization, ensuring that departments work cohesively towards common goals.
Types of ERP Systems
ERP systems come in various forms, tailored to meet the diverse needs of organizations across different industries. Understanding the different types of ERP can help businesses select the most suitable solution for their operations. The main types of ERP systems include:
- On-Premise ERP: This type of ERP is installed locally on a company’s servers and managed by its IT staff. It offers greater control over data security and customization but often requires significant upfront investment in hardware and software.
- Cloud-Based ERP: Offered as Software as a Service (SaaS), cloud-based ERP systems are hosted on the vendor’s servers and accessed via the internet. This model provides flexibility, scalability, and reduces the need for extensive on-site IT infrastructure.
- Hybrid ERP: Combining elements of both on-premise and cloud-based systems, hybrid ERP allows businesses to utilize the advantages of both models. Organizations can keep sensitive data on-premise while leveraging cloud resources for scalability.
- Industry-Specific ERP: This type of ERP is designed with specialized features tailored to specific industries such as manufacturing, retail, healthcare, or construction. These systems address unique operational challenges and compliance requirements of particular sectors.
- Open Source ERP: Open source solutions allow businesses to access and modify the software code. This flexibility helps organizations customize their ERP systems to fit specific needs without incurring high licensing fees.
Importance of ERP in Modern Businesses
The significance of ERP systems in contemporary business environments cannot be understated. They play a crucial role in fostering efficiency and facilitating growth. Key reasons for the importance of ERP include:
- Enhanced Data Accuracy: By centralizing data, ERP systems minimize errors and discrepancies, leading to more reliable information for decision-making.
- Improved Collaboration: ERP systems break down silos between departments, promoting communication and collaboration across the organization.
- Streamlined Operations: Automation of repetitive tasks and processes reduces manual work, allowing employees to focus on value-added activities.
- Scalability: As businesses grow, ERP systems can scale to accommodate increased operations and complexity, supporting expansion into new markets or product lines.
- Regulatory Compliance: ERP systems often come equipped with tools to help organizations adhere to industry regulations and standards, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
“ERP systems serve as the backbone of modern enterprises, integrating various functions into a cohesive framework that drives efficiency and growth.”
By leveraging the capabilities of ERP systems, organizations can not only enhance their operational efficiencies but also position themselves for future success in increasingly competitive marketplaces.
In today’s competitive job market, building a personal brand for job success is crucial. By strategically showcasing your unique skills and experiences, you can differentiate yourself from others. Networking plays a significant role in this process, as establishing meaningful connections can open doors to new opportunities. Therefore, investing time in personal branding can lead to significant advancements in your career.
ERP Implementation Strategies
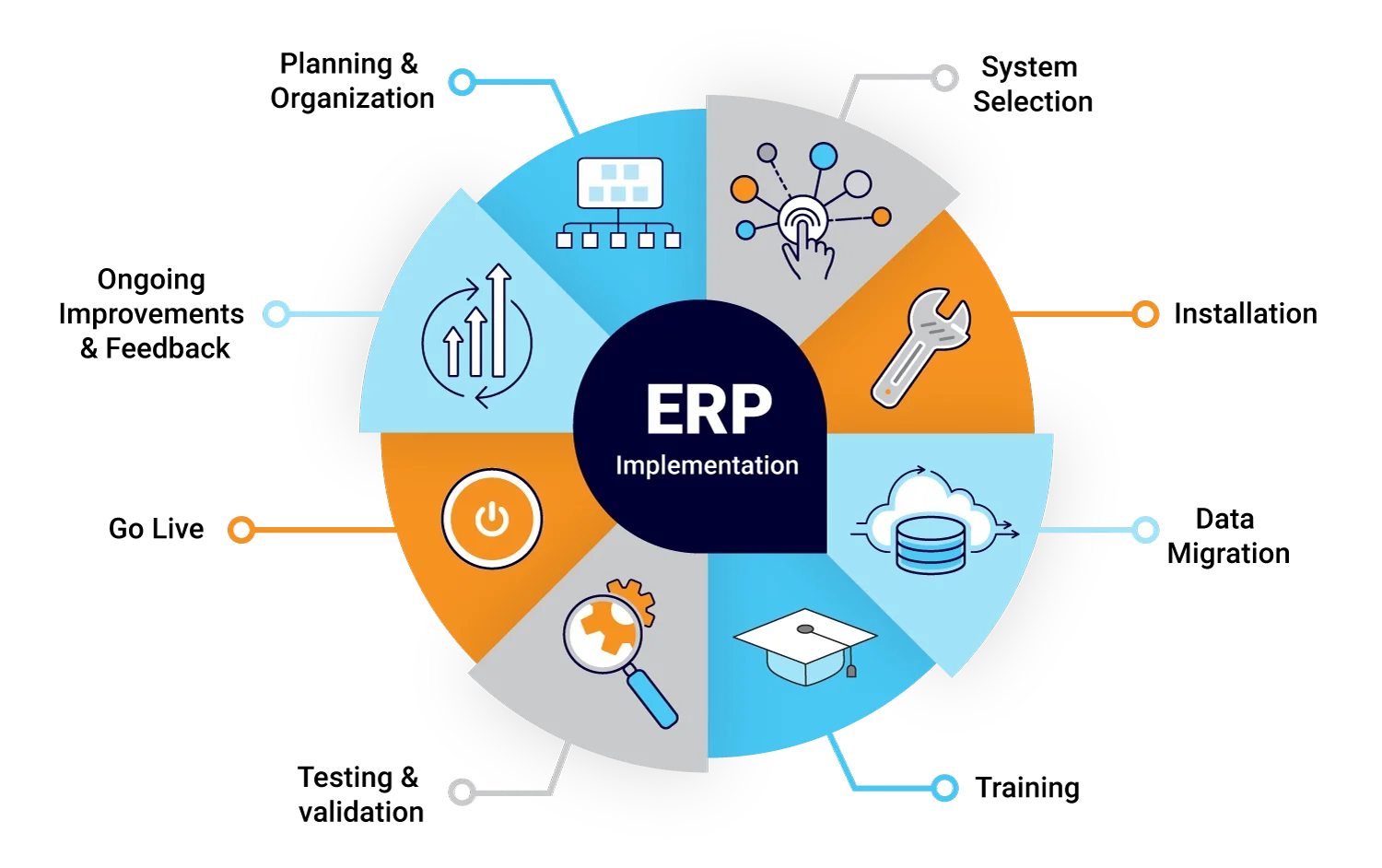
The implementation of an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is a significant endeavor for any organization. A successful ERP deployment can streamline operations, enhance data visibility, and improve overall efficiency within the company. However, careful planning and execution are essential to navigate the complexities of this process.Several key steps are involved in ensuring a successful ERP implementation. Each of these steps plays a crucial role in aligning the ERP system with the organization’s objectives and requirements.
Key Steps for Successful ERP Implementation
The process of implementing an ERP system can be divided into several critical phases. These include:
- Project Planning and Preparation: Establish a project team, define the scope, and set clear objectives. This phase is crucial for laying down the groundwork and ensuring all stakeholders are aligned with the implementation goals.
- Requirements Analysis: Conduct a thorough analysis of business requirements. Understanding the specific needs of different departments will guide the customization and configuration of the ERP system.
- System Selection: Evaluate and select an ERP vendor that best fits the organization’s needs and budget. Consider factors such as functionality, scalability, and support services.
- Data Migration: Prepare and migrate existing data into the new ERP system. This step requires careful planning to ensure data accuracy and integrity during the transition.
- Customization and Configuration: Customize the ERP system to fit the unique business processes of the organization. This may involve adjusting workflows, reporting tools, and user interfaces.
- Testing: Perform comprehensive testing to identify and resolve issues before going live. This includes unit testing, system testing, and user acceptance testing.
- Training and Change Management: Provide training to users to facilitate a smooth transition. Change management strategies should also be developed to address any resistance to the new system.
- Go-Live and Support: Launch the ERP system and ensure that support is available to address any immediate post-implementation challenges. Continuous monitoring and optimization should follow.
Potential Challenges Faced During ERP Deployment
Despite meticulous planning, organizations often encounter several challenges during ERP deployment. Understanding these potential issues can help in devising strategies to mitigate them.Some common challenges include:
- Resistance to Change: Employees may be hesitant to adapt to a new system, leading to potential disruptions in operations.
- Data Quality Issues: Migrating inaccurate or incomplete data can result in functionality problems and misinformed decision-making.
- Underestimating Time and Costs: Organizations may face budget overruns and timeline delays if the scope of the project is not accurately assessed.
- Lack of User Engagement: Insufficient involvement from end-users during the implementation can lead to a system that does not meet actual business needs.
Checklist for ERP Implementation
For businesses planning to implement an ERP system, having a structured checklist can be invaluable for ensuring all critical components are considered. This checklist serves as a guide to facilitate a comprehensive implementation process.
Demonstrating proper workplace etiquette and professionalism tips is essential for fostering a harmonious environment that enhances overall success. By adhering to these guidelines, employees can build positive relationships, communicate effectively, and create a culture of respect. This not only contributes to individual career growth but also strengthens team dynamics, making it vital for anyone aiming to excel in their professional journey.
- Define project goals aligned with business objectives.
- Assemble a dedicated project team with defined roles and responsibilities.
- Conduct stakeholder analysis and gather requirements.
- Research and select the appropriate ERP vendor and solution.
- Create a data migration strategy to ensure data integrity.
- Develop a detailed project timeline with milestones.
- Plan for user training and support initiatives.
- Establish a change management strategy to address cultural shifts.
- Schedule regular progress reviews with stakeholders.
ERP Modules and Features

Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are comprehensive software solutions designed to streamline and integrate various business processes across an organization. These systems consist of multiple modules, each tailored to manage specific functions, which can drastically enhance efficiency and productivity. Understanding these modules and their features is essential for businesses aiming to leverage ERP to its fullest potential.
Core ERP Modules
ERP systems typically encompass several core modules, each serving a distinct function that contributes to the overall efficiency of business operations. Below are the key modules commonly found in ERP systems:
- Financial Management: This module manages the organization’s financial data, including accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting. It ensures compliance with regulatory standards and provides real-time financial insights.
- Human Resources Management (HRM): This module oversees employee records, recruitment, payroll, performance management, and benefits administration, facilitating effective workforce management.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): This module optimizes the flow of goods and services, from procurement to production and distribution, helping to reduce costs and improve product delivery.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): The CRM module focuses on managing interactions with current and potential customers, enhancing customer satisfaction, and driving sales through improved communication and service.
- Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP): This module assists manufacturers in planning production schedules, managing inventory levels, and forecasting demand, ensuring efficient use of resources.
- Project Management: This module enables organizations to plan, execute, and monitor projects effectively, ensuring that they are completed on time and within budget.
Industry-Specific ERP Features
Different industries benefit from tailored ERP features that address their unique operational needs. For example:
- Manufacturing: ERP systems in manufacturing often include advanced production scheduling tools and quality control modules that help optimize production processes and ensure product quality.
- Retail: In retail, ERP features may include point-of-sale (POS) integration, inventory management, and customer analytics, enhancing the shopping experience and optimizing inventory levels.
- Healthcare: The healthcare sector often utilizes ERP systems with modules for patient management, compliance tracking, and supply chain management, which help maintain regulatory standards and improve patient care.
- Construction: ERP systems for construction firms may include project management tools, contract management, and equipment tracking, facilitating efficient project execution and resource allocation.
Customization of ERP Modules
Customizing ERP modules to fit specific business needs is a significant advantage of ERP systems. Customization can enhance usability and ensure that the software aligns with the organization’s workflow. Key aspects of customization include:
- Workflow Adjustments: Organizations can modify workflows within modules to match their operational processes, ensuring that the ERP system complements rather than disrupts existing practices.
- Feature Additions: Businesses may choose to add specialized features or tools that address their specific needs, such as advanced analytics or industry-specific compliance modules.
- User Interface Modifications: Customizing the user interface can improve user experience, making it easier for employees to navigate the system and access the information they need.
- Integration with Other Systems: ERP systems can be integrated with other software applications, such as e-commerce platforms or third-party logistics services, providing a seamless flow of information across various business functions.
“Customization of ERP modules can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your business processes, leading to improved productivity and efficiency.”
In summary, ERP modules serve as the backbone of integrated business management, offering industries tailored solutions to optimize operations and support growth. By customizing these modules, organizations can ensure that their ERP system meets the unique demands of their industry and enhances overall performance.
Future Trends in ERP
As the landscape of business technology continues to evolve, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are poised for transformative changes driven by emerging technologies. The future of ERP will be characterized by greater integration, automation, and intelligence, enabling organizations to enhance efficiency and decision-making in unprecedented ways.Emerging technologies such as cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain are redefining how ERP systems operate.
Cloud-based ERP solutions are gaining traction due to their scalability, flexibility, and lower upfront costs. This shift allows businesses to access real-time data and analytics from anywhere, facilitating faster decision-making. IoT integration enables ERP systems to gather data from connected devices, providing insights that can optimize supply chain management and production processes. Additionally, blockchain technology enhances data security and transparency, particularly in transactions and record-keeping.
Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in ERP Evolution
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are critical drivers of innovation in ERP systems. These technologies enable organizations to automate routine tasks, analyze large datasets, and derive actionable insights with unprecedented speed and accuracy. The incorporation of AI and ML can elevate ERP functionalities in several ways:
- Predictive Analytics: Utilizing historical data, AI algorithms can forecast future trends, helping businesses to make informed decisions and anticipate market changes.
- Enhanced User Experience: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can streamline user interactions with ERP systems, providing real-time support and reducing the burden on human resources.
- Automated Workflow: ML models can identify inefficiencies in business processes, enabling automated adjustments that enhance productivity and reduce operational costs.
- Personalized Reporting: AI can tailor reports to individual user preferences, ensuring that stakeholders receive relevant information without sifting through unnecessary data.
The future of ERP systems will see AI and ML capabilities becoming standard features, driving significant improvements in operational efficiency and strategic planning.
Predictions for ERP Transformation in the Next Decade
As we look ahead to the next decade, several key transformations are anticipated in the realm of ERP systems, influenced by ongoing technological advancements and shifting business needs. Organizations will likely experience:
- Increased Integration with Third-Party Applications: ERP systems will seamlessly connect with various third-party applications, creating a unified ecosystem that enhances data flow and business intelligence.
- Greater Focus on Sustainability: ERP systems will evolve to include features that help businesses track and reduce their environmental impact, integrating sustainability metrics into core operations.
- Enhanced Data Security Measures: As cyber threats become more sophisticated, ERP systems will adopt advanced security protocols, including biometric authentication and enhanced encryption methods.
- Expansion of Mobile ERP Solutions: With the rise of remote work, mobile ERP applications will become increasingly sophisticated, enabling users to access critical information and perform business functions on-the-go.
The integration of these trends will empower organizations to respond swiftly to market dynamics, improve operational efficiencies, and drive growth in an increasingly competitive landscape. As ERP systems continue to evolve, they will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of business management and strategy.